Breakup of Supercontinent Pangea Cooled Mantle and Thinned Crust
January 17, 2017
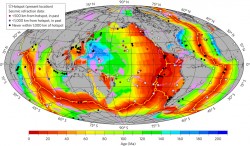
The oceanic crust produced by the Earth today is significantly thinner than crust made 170 million years ago during the time of the supercontinent Pangea, according to University of Texas at Austin researchers.
The thinning is related to the cooling of Earth’s interior prompted by the splitting of the supercontinent Pangaea, which broke up into the continents that we have today, said Harm Van Avendonk, the lead author of the study and a senior research scientist at The University of Texas Institute for Geophysics. The findings, published in Nature Geosciences on Dec. 12, shed light on how plate tectonics has influenced the cooling of the Earth’s mantle throughout geologic history.
Astrobiology Magazine, Dec. 16, 2016
Featuring: Harm Van Avendonk, senior research scientist, Institute for Geophysics, Jackson School of Geosciences
Joshua “Bud” Davis, Ph.D. student, Jackson School of Geosciences
Jennifer Harding, Ph.D student, Jackson School of Geosciences