CT Scan and 3-D Print Help Scientists Reconstruct an Ancient Mollusk
September 19, 2012

Using a combination of traditional and innovative model-building techniques, scientists in the U.S. and a specialist in Denmark have created a lifelike reconstruction of an ancient mollusk, offering a vivid portrait of a creature that lived about 390 million years ago, and answering questions about its place in the tree of life, as described in the Sept. 18 edition of the journal Palaeontology.
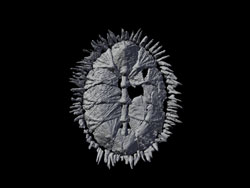
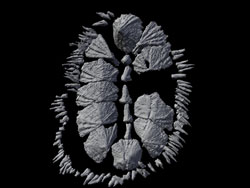
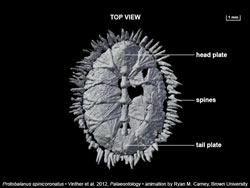
The model of the oval-shaped sea creature, called a multiplacophoran, which was covered with stiff plates and a ring of spines, resulted from a collaboration between Jakob Vinther, a postdoctoral researcher at The University of Texas at Austin’s Jackson School of Geosciences, and Esben Horn, owner of the model making company 10 Tons in Copenhagen (www.10tons.dk), with animation help from Ryan Carney, a doctoral student at Brown University.

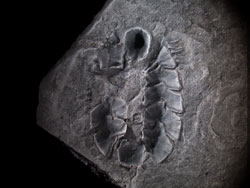
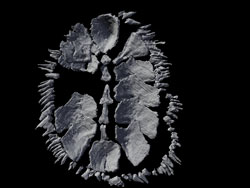
Working with a delicate specimen of a multiplacophoran partially covered by rock, Vinther used a micro CT scan — a noninvasive technology similar to medical CAT scanning — to create a three-dimensional view of the fossil. With Carney’s help, the CT scan yielded an animated view of the original placement of the creature’s dense spines and shells, which had splayed out and decayed prior to fossilization.
The CT scan also produced a three-dimensional cast of the specimen in its reconstructed shape. Working with the cast, the animation and information on living relatives of the multiplacophorans, Horn was able to create a multicolored, textured model in clay, resin and silicone showing how the creature looked millions of years ago, when it crawled on a single, suction-like foot over shells and rocky surfaces in ancient oceans.
The model helps address a debate about how multiplacophorans (which were only discovered in the past decade) relate to chitons, another more widely known plated mollusk that lives on seashores and is commonly eaten in the Caribbean. By dating the origin of modern chitons, Vinther could demonstrate that multiplacophorans are stem group chitons.
“We can now demonstrate that multiplacophorans are distant relatives of the modern chitons, which did not evolve until later in Earth history,” said Vinther. “We can also show that they evolved a number of characteristics seen in some modern chitons convergently.”
The CT scan was integral to the project, allowing the scientists to see below the surface of the fossil.
“CT scanning is an extremely powerful technique for paleontologists,” said Vinther, “since we can look inside fossils without destroying them.”
Vinther and Horn describe the process of creating the model in a video produced by the Jackson School of Geosciences and available from National Geographic.
The original fossil was discovered 10 years ago in Ohio by private collector and co-author George Kampouris, who donated it to the Cincinnati Museum of Natural History.
Also See: “The Origin of Multiplacophorans — Convergent Evolution in Aculiferan Molluscs”, Paleontology, Sep. 18, 2012.
Video
| Prehistoric Movie Monster Mollusk Re-created with 3D Printer (National Geographic) | |
| Animation: CT Scan Reconstruction of Ancient Mollusk |