Ion Concentrations in Reverse Osmosis Membranes
November 17, 2010
Linda Passaniti (MS Candidate)
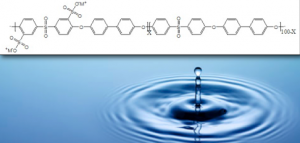
Ion Concentrations in Sulfonated poly(arylene ether sulfone) (BPS) Reverse Osmosis Membranes
Due to the presence of sulfonate groups, BPS acts as an ion exchange membrane, allowing it to separate solute from solvent in part through the preferential transport of cations and near exclusion of anions. ICP-MS data are used to determine partition coefficients for cations in the membrane illustrating, for example, that the concentration of sodium is significantly greater than chloride in a membrane previously equilibrated in a sodium chloride solution. Understanding this is necessary for modeling the transport of sodium chloride through the membrane during the reverse osmosis purification of brackish and sea water. Such data also improve understanding of how membrane morphology affects its water flux and salt exclusion properties.