NSF Grant
Hurricane Helene (2024) Rainfall, Brown Ocean Signature, AI and Physics Model Guidance, and Social Media Sentiment
Project Description
We are trying to address four questions: (i) How much did it rain during Hurricane Helene? (ii) Was this a “poster storm for brown ocean effect”? (iii) What were the AI/ML based models predicting for the inland conditions, relative to the classical physics- based models?, and (iv) What was the public sentiment before the storm moved inland?
Team Members
Dev Niyogi, Hassan Dashtian, Manmeet Singh, Alka Tiwari, Sasanka Talukdar, Adil Waheed
i) Rainfall Variability
Our primary focus will be to determine how much rain occurred during Helene’s passage and how this rainfall varied spatially and temporally. We will use Stage IV radar-gauge merged precipitation products, from NASA’s Global Precipitation Mission (GPM) – the Integrated Multi-satellite Retrievals (IMERG) and interpolated COOP in-situ precipitation estimates.
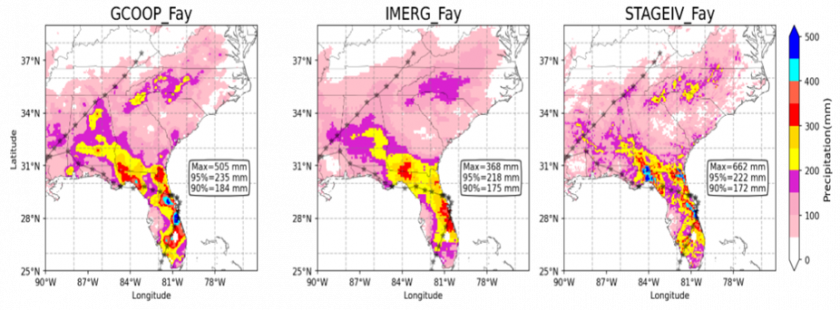
Total precipitation accumulation from interpolated in-situ COOP (GCOOP), estimates form IMERG and radar QPEs Stage IV for a TC which had similar track to TC Helene 2024.
