DISCUSSION
Discussion and findings
In this project, two primary factors were examined for their influence on the precision and accuracy of ICP-MS measurements of REE concentrations: the dilution factor and the choice of CRC operating mode (no-gas mode vs O₂ mass-shift mode).
Overall, the two modes produced similar trends for most REEs. Concentrations measured in O₂ mode were consistently 20–40% higher than those obtained in no-gas mode, with the discrepancy reaching as high as 95% for Nd. A similar pattern was observed in the QCs, where element recoveries were systematically over-reported under O₂ mode. This behavior arises because under O₂ mode, not only REEs but also many matrix ions undergo oxidation in the reaction cell, generating additional signal at the REE–oxide mass positions. Although isotopes and oxide mass-shift pairs were selected carefully to minimize interferences between LREEs and HREEs, certain overlaps remain, namely 142Nd16O⁺ with 158Gd⁺, 153Eu¹⁶O⁺ with 169Tm⁺, 159Tb16O+ with 175 Lu+. which contributes to the pronounced concentration over-reporting of Nd in O₂ mode. Moreover, while O₂ significantly reduces the BEC, the reaction cell simultaneously produces additional oxide ions from matrix and impurity elements. These oxide products amplify background signals under the low-BEC conditions and introduce reaction-efficiency mismatches between standards and QC matrices, ultimately leading to a systematic positive bias across all REEs in O₂ mode.
Light REEs:

Heavy REEs:

Several elements, including Eu and Yb showed different results under O2 mode. Eu exhibited that concentrations in no-gas mode were ~14% higher than those in O2 mode. Yb showed unusually large standard deviations in O₂ mode. It has been reported that the production ratios of EuO⁺ and YbO⁺ are significantly lower than those of other REE oxides because EuO⁺ and YbO⁺ formation reactions are endothermic, whereas those of most other REEs are exothermic. Applying a more negative voltage only marginally yields Eu and Yb oxide ion (Zhu, 2018; Zhu, 2021). Therefore, researchers have used N₂O rather than O₂ as the reaction gas to improve EuO⁺ and YbO⁺ production. U also behaved anomalously in O₂ mode. Under O2 conditions, UO⁺ tends to undergo further oxidation to form the more stable UO₂⁺ ion. Therefore, M→M+32 (238 → 270) mass shift should be used here instead of M→M+16 (238 → 254).
About dilution factor, results show that for Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Dy, Ho, Y, Tm, and Th, dilution had minimal impact on the measured concentrations in either mode. The standard deviation generally remained below 5% and the averages were more consistent with concentration results from DF=1000 and 5000. At these dilutions, REEs concentrations fall within ~0.1–2 ppb. Based on blank measurements, the LODs of most REEs were approximately 0.003 ppb, whereas Sc, Y, and Th were slightly higher LODs (~0.01 ppb). This suggests that when REE concentrations are ~50–500× above the LOD, high analytical accuracy can be achieved.
Sc and Lu displayed poor accuracy in both modes. Their measured concentrations increased with dilution factor, despite remaining within the instrument’s acceptable range (<200 ppb and >LOD). This trend indicates significant contamination, matrix effects or spectral interference in the measurements of Sc and Lu, and re-analysis is required.
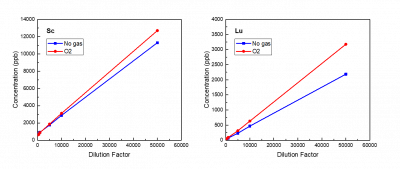
By plotting concentration versus dilution factor on a linear scale rather than a log scale, it becomes evident that the concentrations of Sc and Lu increase linearly with the increase of dilution factor. This trend might arise from contamination introduced during dilution, possibly due to trace amounts of Sc and Lu present in the 2% HNO3 used for dilution. However, the issue still remains to some extent, since theoretically the same acid was used to dilute the calibration standards and QCs and their results remained within acceptable ranges.
Besides, previous studies have reported that high Si concentrations in the matrix can cause spectral interference on Sc (Li, 2017). However, this effect was not manifested in the present study. The high dissociation energy of the Si–O bond, together with the high natural isotopic abundance of silicon, facilitates the formation of highly stable silicon oxide species (e.g., 28Si17O⁺, 29Si16O⁺). Therefore, accurate determination of Sc may require simultaneous measurement of Si and subsequent interference-equation correction when Si cannot be effectively removed during sample pretreatment.
Considering the combined influences of operating mode and dilution, no gas mode with a dilution factor of 1000–5000 is recommended for Y, La, Ce, Pr, Nd, Sm, Eu, Gd, Tb, Dy, Ho, Er, Tm, Th, and U. For Yb, O2 mode currently yields more reliable values. Future analyses may benefit from using N₂O as the reaction gas for Eu and Yb, and from using the 238 → 270 mass-shift pair for U. For Sc and Lu, due to large variability, will require new measurements under revised conditions. Further measurements should also include the concentrations of major ions, particularly Si, to enable interference-equation based corrections in subsequent data processing.
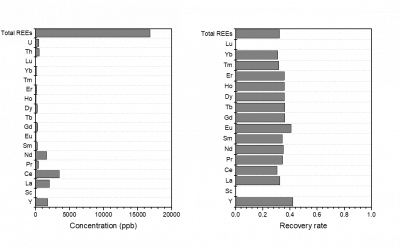
The figure above plots the final REE concentrations and recovery rate. Results show that the using 12M HNO3 as leaching reagent, a relatively low total REEs recovery rate (~30%) is achieved, indicating that HNO3 is not the most suitable acid for extracting REEs from this CFA. A stronger acid capable of bulk matrix dissolution is needed here. Nonetheless, by discussing how ICP-MS mode and dilution factor influence REE quantification in complex CFA leachates, this project provides some mechanistic insight for developing methods for REE measurement using ICP-MS.
Cost
Before testing, the estimated cost was $840. During actual measurements, we analyzed the following sample sequence:
6 calibration standards → 2 QCs → 1 blank → 1 QC → 1 blank → 5 samples → 1 blank → 1 QC → 1 blank,
resulting in a total of 19 analyses and a final cost of $380, which is within the initial budget.