New Shale Gas Drilling Methods Boost Production Potential, Study Finds
December 17, 2018
A new analysis of the nation’s major shale gas plays has revealed that the amount of natural gas that can be technically recovered from future well locations has increased by 20 percent compared with an estimate made about five years ago, even while active drilling has depleted the resource. Researchers attributed the increase largely to new drilling practices.
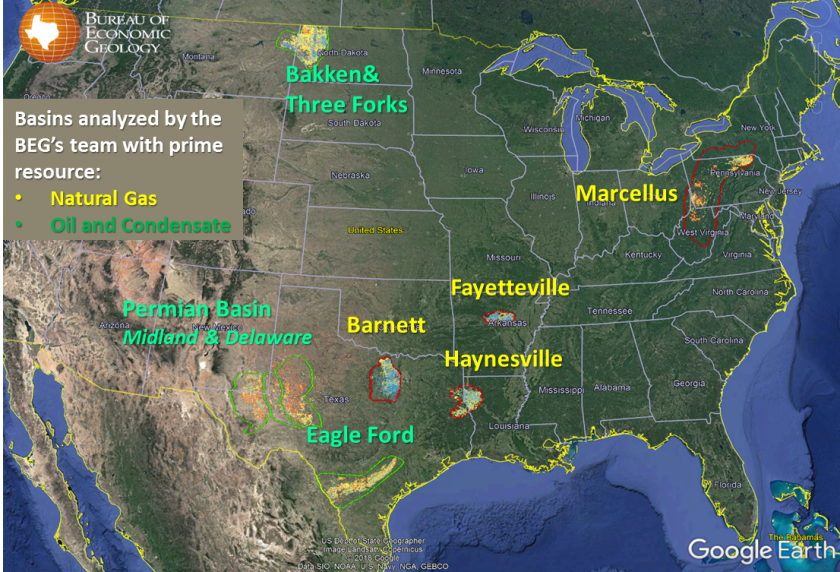
The analysis, conducted by the University of Texas at Austin’s Bureau of Economic Geology, looked at the production capabilities and the total gas in place of four of the country’s top natural gas fields: the Barnett, Fayetteville, Haynesville and Marcellus plays. It is an update of a similar study the bureau conducted from 2011 to 2013 that was the most comprehensive report on unconventional resources publicly available at the time.
Svetlana Ikonnikova, the principal investigator of the study and a research scientist at the bureau, said that developments in drilling technologies, market conditions, cost structures and improvement in geological characterization prompted the research team to update the assessment.
“Five years ago, we hardly thought of multilayer or stacked well drilling, or of quadrupling lateral well length,” she said, referring to drilling innovations that have expanded production.
The team used 3D modeling and advanced data analytics to enhance the understanding of:
- Geologic reservoir characterization;
- Individual well decline and recovery analysis;
- Individual well geology and engineering improvements that increase productivity; and
- Economically recoverable resource assessment.
The researchers found that future wells in the four shale gas plays can technically recover about 780 trillion cubic feet (Tcf) of natural gas, in addition to about 110 Tcf of gas already recovered by wells drilled by the end 2017. (“Technically recoverable” gas can be produced using currently available technology and industry practices.) That estimate was about 650 Tcf in the previous study. The United States consumed about 27 Tcf of natural gas in 2017, so the new estimate suggests the addition of about five years of domestic consumption.
The projected increase comes largely from new drilling practices that increase recovery, reduce per-unit cost and allow companies to continue drilling even during periods of low oil or natural gas prices. These new methods include stacked drilling, which accesses gas by expanding the vertical reach of fracturing. Drilling wells closer together and installing wells that can run horizontally for about two miles has further improved recovery.
Researchers also calculated the total gas held in the four shale plays to be 3,100 Tcf. Katie Smye, co-principal investigator of the study and bureau geologist, said it’s important to understand the amount of gas-in-place to verify what proportion has been recovered, compare results across plays and determine where additional wells can be drilled and efficiency can be improved.
For instance, in the Haynesville and Marcellus plays, only 2 to 3 percent of the total gas-in-place is expected to be recovered by wells drilled to date, Smye said. This percentage is influenced by a number of factors including technology, economics and the amount of the play available for drilling.
“The Marcellus contributes the majority of the gas-in-place due to its size and resource density,” Smye said. “However, resource density in the Haynesville is comparable to the best areas in the Marcellus.”
In the study, for the base case scenario, researchers assumed a natural gas price of $3.25 per million British thermal units (MMBtu) and an oil price of $65 per barrel. Despite being lower than price assumptions from the past analysis, these prices yielded a 20 percent increase in natural gas supply compared with the base case scenario in the original study. Researchers also ran scenarios at lower prices, using a natural gas price of $2.75 per MMBtu and an oil price of $50 per barrel, and at higher prices, using $4.50 per MMBtu and $80 per barrel. These scenarios are in line with the range of projections by the Energy Information Administration until about 2030.
Even with the boost in production, the analysis shows production will plateau around 2030, barring a more dramatic price increase or boost in technology.
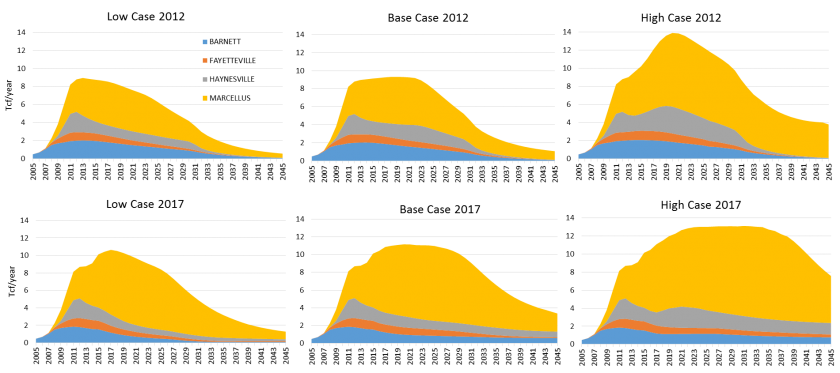
Researchers said this analysis emphasized the need to better understand cross-play dynamics in terms of capital allocation and investment decision making. Sharp declines in drilling and production from the Barnett and Fayetteville shales imply that these plays have matured, although they may simply be less attractive in terms of return on investment relative to other plays, especially those with more liquids production. The bureau’s Tight Oil Resource Assessment consortium has been focusing on the Permian Basin, which has been attracting the most investment in recent years.
The bureau is part of the UT Jackson School of Geosciences and is the State Geological Survey of Texas. Its 15-member interdisciplinary Shale Production and Reserves Study team integrates engineering, geology and economics. Peer-reviewed studies of the report’s technical analyses will be published in the coming months. The study was funded by the U.S. Department of Energy National Energy Technology Laboratory.
The University of Texas at Austin is committed to transparency and disclosure of all potential conflicts of interest of its researchers. All of the shale gas play research team members have filed required disclosures. Co-Principal Investigator Scott Tinker sits on the Shell Science Council and serves on government boards and commissions dealing in energy issues. Team members Robin Dommisse and Bill Fisher hold stock in oil and gas companies. Dommisse, Scott Hamlin and Ken Medlock occasionally consult for oil and gas companies and/or for government entities on energy topics. Michael Marder is currently receiving funding from Shell through the Shell-UT Unconventional Research program. The university is not aware of potential conflicts of interest for any of the other team members. The Jackson School itself receives annual income from royalties on shale gas reserves donated to the university.